Becquerel, AntoineHenri, Biography Abstract Henri Becquerel was a nuclear physicist at the École Polytechnique, specializing in radiation and radioactivity He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1903 "in recognition of the extraordinary services he has rendered by his discovery of spontaneous radioactivity" Important DatesThe mark of a great scientist is making grand discoveries almost unintentionally While studying fluorescence, Henri Becquerel discovered natural radioactiviAntoine Henri Becquerel (15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French physicist, Nobel laureate, and the discoverer of radioactivity along with Marie SkłodowskaCurie and Pierre Curie, for which all three won the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics Antoine Henri Becquerel (15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French physicist, Nobel laureate, and the discoverer of radioactivity

Henri Becquerel S Discovery Of Radioactivity 125 Years Later Physica Medica European Journal Of Medical Physics
Antoine henri becquerel discovery
Antoine henri becquerel discovery- Antoíne Henri Becquerel (1852–1908), Fig 1, was a third generation physicist in a family of wellknown, respected 19th century physicists , , The long family tradition in science started with Henri's grandfather AntoíneCésar Becquerel (17–1878), who after a short career in the Napoleon army, had a successful career as a researcher in physics and chemistry until hisHenri Becquerel Antoine Henri Becquerel () was a French physicist and winner of the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics Becquerel was born in Paris, France on He was the son of a professor of applied physics, Alexander Becquerel He began his studies in 1872 at École Polytechnique just south of Paris




Henri Becquerel High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
Antoine Henri Becquerel (15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French physicist, Nobel laureate, and the discoverer of radioactivity, for work in this fie Becquerel was a member of one of science's most distinguished families From Napoleon the First to World War II, male members of four generations dedicated their lives to research, with each producing important discoveries Henri's grandfather, Antoine Cesar Becquerel, invented a method of extracting metals from ores using electrolysisThe full impact of Becquerel's discovery was not appreciated, however, until the work of Marie and Pierre Curie, with whom he shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in physics Henri's son Jean Becquerel also became a physicist, and four generations of Becquerels were educated at the École Polytechnique and became professors of physics at the French
1852–1908 AntoineHenri Becquerel was born the son of the physicist AlexandreEdmond Becquerel, and the grandson of the physicist AntoineCésar Becquerel, and it is not surprising that he followed in their footsteps It is also not surprising that his research interests centered around solar radiation and phosphorescence, as these areAntoineHenri Becquerel () is known for his discovery of radioactivity, for which he received the Nobel Prize for Physics jointly with Marie Curie () and Pierre Curie () in 1903 and the contributions he made to that field What did Antoine Henri Becquerel discover?
This year it is 125 years since Henri Becquerel accidentally discovered radioactivity It has been argued that this was the result after Becquerel's long, systematic research into the phenomenon of luminescence Becquerel's discovery, together with Marie and Pierre Curie's discovery of radium, became the breakthrough for the th century15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French engineer, physicist, Nobel laureate, and the first person to discover evidence of radioactivityFor work in this field he, along with Marie SkłodowskaCurie (Marie Curie) and Pierre Curie, received the 1903 Nobel Prize in PhysicsThe SI unit for radioactivity, the becquerel (Bq), is named4 Shimizu S Henri Becquerel, AntoineHenri Becquerel (1852– 1908) discovery of radioactivity (16) centenary year, Japan Radioisotope Association 1996;1–12 5 O¯ ba S Centennial of the discovery of radium Marie Curie and Pierre Curie NichiDoku Iho 1998;43(4)97–123 5 See Ref 4 Sakae Shimizu, 7 6 See Ref 2 Shozo Hashimoto



Biography Of Henri Becquerel




Art And Architecture Mainly Dr Marie Curie My Greatest Medical Hero Guest Post
Antoine Henri Becquerel () is known as the man who discovered radioactivity—a discovery that influenced the development of atomic weapons, nuclear energy, and radioactive medical treatments Becquerel was born on , in Paris, France Both his father, Alexandre Edmond Becquerel, and his grandfather, Antoine Cesar Becquerel, one of the In 1908 the discoverer of radioactivity, Henri Becquerel, died, and in the same year Ernest Rutherford was awarded the Nobel prize in chemistry for his work on radioactivity In Short Becquerel's pioneering work on radioactivity led to Rutherford's work, among others', on the disintegration of the elements AntoineHenri Becquerel was born in AntoineHenri Becquerel was born in Paris in a wealthy family that produced four generations of physicists Becquerel's grandfather (Antoine César Becquerel), the father (AlexandreEdmond Becquerel) and the son (Jean Becquerel) Henri Becquerel began his education by attending Lycée LouisleGrand, a preparatory school in Paris He studied




Henri Becquerel Youtube




Henri Becquerel French Physicist Britannica
PLAY Match Gravity Antoine Henri Becquerel Click card to see definition 👆 Tap card to see definition 👆 In 16, while investigating uranium salts, Becquerel accidentally discovered radioactivity Becquerel found that the photographic plates were fully exposed when in contact with radioactive salt Click again to see term 👆Discovery of Gamma Rays Antoine Henri Becquerel Gamma rays were discovered shortly after the discovery of Xrays In 16, French scientist Henri Becquerel discovered that uranium minerals could expose a photographic plate through another material Becquerel presumed that uranium emitted some invisible light similar to Xrays, which WCRoentgen recently discoveredHenri Becquerel, in full AntoineHenri Becquerel, (born , Paris, France—died , Le Croisic), French physicist who discovered radioactivity through his investigations of uranium and other substances In 1903 he shared the Nobel Prize for Physics with Pierre and Marie Curie He was a member of a scientific family extending through several
/fStopImages-JuttaKuss-5c01fe3446e0fb0001ddc127.jpg)



Henri Becquerel And The Discovery Of Radioactivity




Antoine Henri Becquerel 1852 1908 French Physicist For His Discovery Of Spontaneous Radioactivity Famous Scientist Physicist Physicists
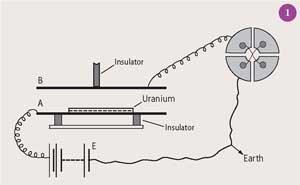
The Discovery of Radioactivity In 16 Henri Becquerel was using naturally fluorescent minerals to study the properties of xrays, which had been discovered in 15 by Wilhelm Roentgen Becquerel used an apparatus similar to that displayed below to show that the radiation he discovered could not be xraysWhen Henri Becquerel investigated the newly discovered Xrays in 16, it led to studies of how uranium salts are affected by light By accident, he discovered that uranium salts spontaneously emit a penetrating radiation that can be registered on a photographic plate Radioactivity was discovered in 16 by the French scientist Henri Becquerel while studying the natural phosphorescence of substances Using samples that contained uranium, Becquerel noted that radioactive emissions occurred spontaneously The main types of radioactivity are alpha, beta and gamma emissions Many studies carried out before and after




Antoine Henri Becquerel High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Becquerel Unit
Becquerel, AntoineHenri () French physicist AntoineHenri Becquerel's landmark research on x rays and his discovery of radiation laid the foundation for many scientific advances of the early twentieth centuryX rays were discovered in 15 by the German physicist Wilhelm Conrad R ö ntgen, and in one of the most serendipitous events inHenri Becquerel Antoine Henri Becquerel () Henri Becquerel was born into a family of scientists His grandfather had made important contributions in the field of electrochemistry while his father had investigated the phenomena of fluorescence and phosphorescence What did Henri Becquerel discover about the atomic theory?




Antoine Henri Becquerel




Henri Becquerel Biography Discovery Study Com
, was the birthday of French physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel, who discovered a completely unknown property of matter in March 16 Becquerel Some might say Becquerel's discovery of "radioactivity" was a lucky accidentbut as the Roman philosopher Seneca wrote in the 1st century, "Luck is what happens when preparation meets Henri Becquerel Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this websiteWhen Henri Becquerel investigated the newly discovered Xrays in 16, it led to studies of how uranium salts are affected by light By accident, he discovered that uranium salts spontaneously emit a penetrating radiation that can be registered on a photographic plate




Antoine Henri Becquerel Father Of Nuclear Energy




Classroom Notes For Radiation And Life 98 101
Biography of Antoine Henri Becquerel () French physicist born in Paris on and died on in Le Croissic Member of one of the most illustrious scientific dynasties of France, in 1903 was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics he/she shared with Pierre () and Marie Curie () the discovery of natural radioactivityAntoine Henri Becquerel (/ ˌ b ɛ k ə ˈ r ɛ l /; Antoine Henri Becquerel (15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French physicist, Nobel laureate, and the first person to discover evidence of radioactivity Henri Becquerel – Biographical – Nobelprizeorg Antoine Henri Becquerel was born in Paris on , a member of a distinguished family of scholars and scientists




Henri Becquerel S Discovery Of Radioactivity 125 Years Later Physica Medica European Journal Of Medical Physics




Facts On The Man Who Discovered Radioactivity And Shared The Nobel With Marie And Pierre Curie Education Today News
Henri Becquerel Biographical A ntoine Henri Becquerel was born in Paris on , a member of a distinguished family of scholars and scientists His father, Alexander Edmond Becquerel, was a Professor of Applied Physics and had done research on solar radiation and on phosphorescence, while his grandfather, Antoine César, had been a Fellow of the Royal SocietyAntoine Henri Becquerel On the rays emitted by phosphorescence1 In an earlier session, M Chairman Henry announced that phosphorescent zinc sul de2 placed in the path of rays emanating from a Crookes tube3 augmented the intensity of rays passing through the aluminumAntoine Henri Becquerel Henri Becquerel was born into a family of scientists His grandfather had made important contributions in the field of electrochemistry while his father had investigated the phenomena of fluorescence and phosphorescence Becquerel not only inherited their interest in science, he also inherited the minerals and compounds



Discovery Of Radioactivity Becquerel




Henri Becquerel Summary Britannica
On an overcast day in March 16, French scientist Antoine Henri Becquerel opened a drawer and found spontaneous radioactivity in one of the most wellknown accidental discoveries in the history of physics Henri Becquerel was in a good position to make the exciting discovery, which came just a few months after xrays were discovered All Aglow 16 Radioactivity is discovered accidentally by French physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel Becquerel was investigating German colleague Wilhelm Roentgen's work onIn 16 French physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel began his own experiments on Röntgen's Xrays 1 He discovered that certain substances, such as uranyl sulfate, emitted rays with properties similar, though not identical, to those discovered by Röntgen




The Discovery Of Radioactivity




Biography Of Antoine Henri Becquerel My Experiences Biography Health History Science News
In 16, French scientist Antoine Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity which was an early contribution to atomic theory He discovered this phenomenon while experimenting with uranium and a photographic plate Becquerel began his experiment by exposing a crystal that contained uranium to sunlight After the crystal had soaked up some Antoine Henri Becquerel was born in Paris on He was a member of a family of scholars and scientists over four generations, including his grandfather, AntoineCesar Becquerel (), his father, AlexandreEdmond Becquerel (1091), and his own son Jean Becquerel ()Abstract This year it is 125 years since Henri Becquerel accidentally discovered radioactivity It has been argued that this was the result after Becquerel's long, systematic research into the phenomenon of luminescence Becquerel's discovery, together with Marie and Pierre Curie's discovery of radium, became the breakthrough for the th




Henri Becquerel French Physicist Britannica




93 Henri Becquerel Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images
AntoineHenri Becquerel Research Papers 285 Words2 Pages AntoineHenri Becquerel was a major inspiration to me, Marie Curie, and my hardworking husband, Pierre Curie Mr Becquerel motivated the two of us to do our absolute best at each His son, Antoine Henri Becquerel, was one of the people who discovered radioactivity, earning him a Nobel Prize for Physics In addition to that, Becquerel also studied the properties of light He paid special attention to the photochemical effects and spectroscopic characters of solar radiation and electric light




Becquerel Antoine Henri 1852 1908



Henri Becquerel Radioactivity A New Property Of Matter Harper S Magazine August 1902




Henri Becquerel Biography Facts And Pictures




Henri Becquerel French Physicist Stock Image C0 6941 Science Photo Library




Emma Markham Fully Vaccinated Happy 165th Birthday To Antoine Henri Becquerel Who Discovered Radioactivity And Won The Nobel Prize In 1903 Scientistbirthday T Co Rk3uhuhjbj



Worldkings On This Day March 02 21 Antoine Henri Becquerel Discovered Radioactivity In 16 Worldkings World Records Union




Antoine Becquerel A Short Biography



The Discovery Of Radioactivity



Benchmarks Henri Becquerel Discovers Radioactivity On February 26 16




Antoine Henri Becquerel 1852 1908 History Of Science 101




Henri Becquerel Atomic Theory Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Worldkings On This Day March 02 21 Antoine Henri Becquerel Discovered Radioactivity In 16 Worldkings World Records Union




Or Antoine Henri Becquerel Isn T Hard To Remember Is It R Memes



1




Antoine Henri Becquerel Antoine Henri Becquerel 15 12 1852 News Photo Getty Images




Henri Becquerel Students Britannica Kids Homework Help




Ch Radioactivity And Nuclear Chemistry Dr Namphol



Discovery Of Radioactivity Becquerel




Kelvin Institute Antoine Henri Becquerel Was A French Physicist Nobel Laureate And The First Person To Discover Evidence Of Radioactivity The Si Unit For Radioactivity The Becquerel Is Named After Him



Radioactivity Discovered Feature Rsc Education




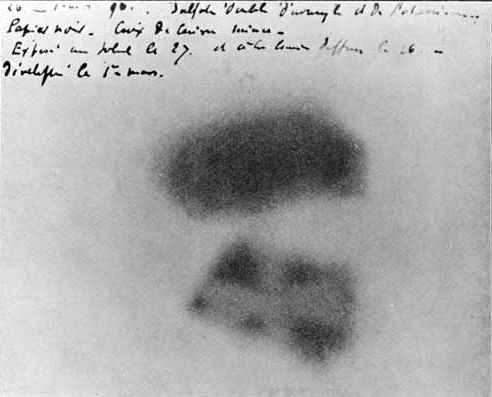
Image Of Antoine Henri Becquerel 1852 1908 French Physicist The Fogged Photographic Plate With Annotations In The Hand Of Becquerel Which Led To His Discovery Of Radiation In 16 From Granger Historical Picture Archive




Henri Becquerel Facts Worksheets Early Life For Kids




Antoine Henri Becquerel Antoine Henri Becquerel 15 12 1852 News Photo Getty Images




Henri Becquerel Wikipedia



Henri Becquerel And Radioactivity Scihi Blogscihi Blog




Henri Becquerel Scientist Of The Day Linda Hall Library




Scientist Information Scientist And Inventions Scientist Biography Scientist Name Photos Image Antoine Henri Becquerel 15 Dec 1852 25 Aug 1908



Biography Of Henri Becquerel Assignment Point



Henri Becquerel By Ana Jaramillo Infographic



3




Introductory Chemistry 3 Rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Chapter




Henri Becquerel French Physicist Britannica




Discoverers Of Radioactivity Group 1 Antoine Henri Becquerel Was A French Physicist Nobel Laureate And One Of The Discoverers Of Radioactivity He Ppt Download




Antoine Henri Becquerel 1852 1908 Beach Towel For Sale By Granger




Ppt Radioactivity Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Henri Becquerel Quotes 5 Science Quotes Dictionary Of Science Quotations And Scientist Quotes




Radioactivity And Types Of Radiation Ppt Download




Henri Becquerel Stock Image H402 0176 Science Photo Library




Discovery Of Radioactivity Introduction To Chemistry




Antoine Henri Becquerel His Part Of The Atomic Theory By Grecia Emberger




Nobelprizeinphysics Antoine Henri Becquerel In Recognition Of The Extraordinary Services He Has R Nobel Prize In Physics Academy Of Sciences Objectives Board




This Month In Physics History



May 16 Chem110 Blogpost




Henri Becquerel French Physicist Britannica




Nuclear Chemistry Radioactivity Antoine Henri Becquerel 1852 1908 Discovered Radioactivity Accidentally While Experimenting With Photographic Film Ppt Powerpoint




Henri Becquerel French Physicist Britannica



Becquerel Antoine Henri 1852 1908 French Physicist Scientist




Radioactivity What Is It Radioactivity Is The Spontaneous




Antoine Henri Becquerel




Henri Becquerel Wikipedia




Ppt Radioactivity Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Marie Curie




Physicist Page Henri Becquerel The Discovery Of Radioactivity On 12 June 1901 The French Physicist Henri Becquerel Was Doing A Demonstration At The Academy Of Sciences Of Paris For A New




Henri Becquerel And The Discovery Of Radioactivity Ans Nuclear Newswire




Nuclear Chemistry Antoine Henri Becquerel February Antoine Henri Becquerel A French Scientist Was Conducting An Experiment Which Ppt Download




Antoine Henri Becquerel French Physicist Stock Image C033 7296 Science Photo Library




Biography Of Henri Becquerel Assignment Point




The Discovery Of Radioactivity That Time The Sun Didn T Shine In Paris United Academics Magazine




Marie Curie Curie En Inventions Inventors Marie Nobel Prize Polonium Science Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters




Henri Becquerel High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




March 1 16 All Aglow Wired




Henri Becquerel Reina Imaging




Henri Becquerel New World Encyclopedia




Scientist Information Scientist And Inventions Scientist Biography Scientist Name Photos Image Antoine Henri Becquerel 15 Dec 1852 25 Aug 1908




History Corner Antoine Henri Becquerel Springerlink
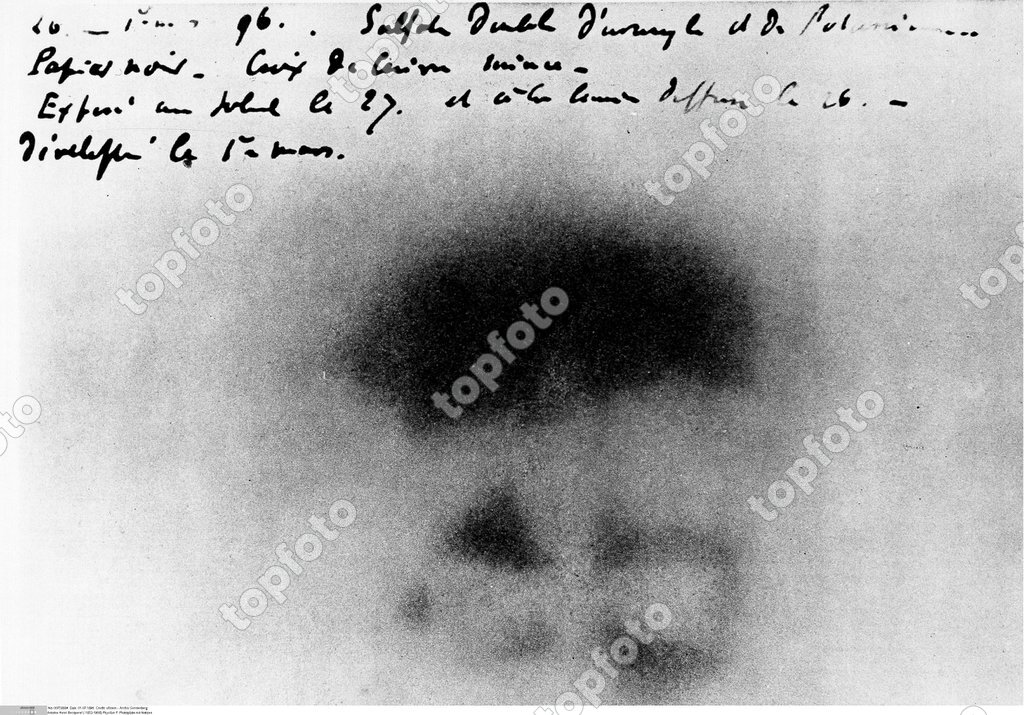



Antoine Henri Becquerel Antoine Henri Becquerel 15 12 1852 25 08 1908 Scientist Physicist France Discovered 16 Nuclear Radiation Of Uranum 1903 Award Of The Nobel Prize With P And M Curie Depiction Of The Photographic
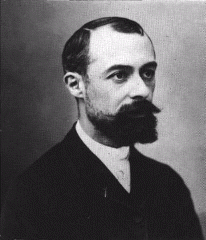



Antoine Henri Becquerel Environmental Health Safety Michigan State University




Radioactivity What Is It Radioactivity Is The Spontaneous




Steam Campus Antoine Henri Becquerel French 15 December 1852 25 August 1908 Was A French Engineer Physicist Scientist Nobel Laureate And The First Person To Discover Evidence Of Radioactivity For



Antoine Henri Becquerel Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure Reaction Salt Atom



Henri Becquerel By Josie J




Atom Discovery Of Radioactivity Britannica




Henri Becquerel Scientist Of The Day Linda Hall Library



French Physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel Signed Letter Lot Heritage Auctions




Henri Becquerel Biography Childhood Life Achievements Timeline




Solved 18 Identify The Scientist S That Were Awarded The Chegg Com
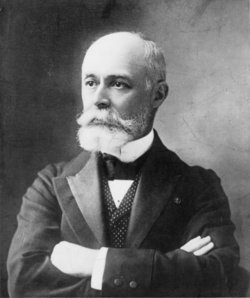



Antoine Henri Becquerel Bragitoff Com




Need To Know Historical Outline Of Radioactivity Work Of Becquerel Discovery Of Radiation From Uranium Salts Marie And Pierre Curie Discovery Of Polonium Ppt Download




Henri Becquerel And The Discovery Of Radioactivity Ans Nuclear Newswire




Radiological Society Of North America Rsna Happy Birthday To Antoine Henri Becquerel Born This Day In 1852 Becquerel Discovered Radioactivity Received The 1903 Nobel Prize In Physics Check Out The




Henri Becquerel Facts Worksheets Early Life For Kids
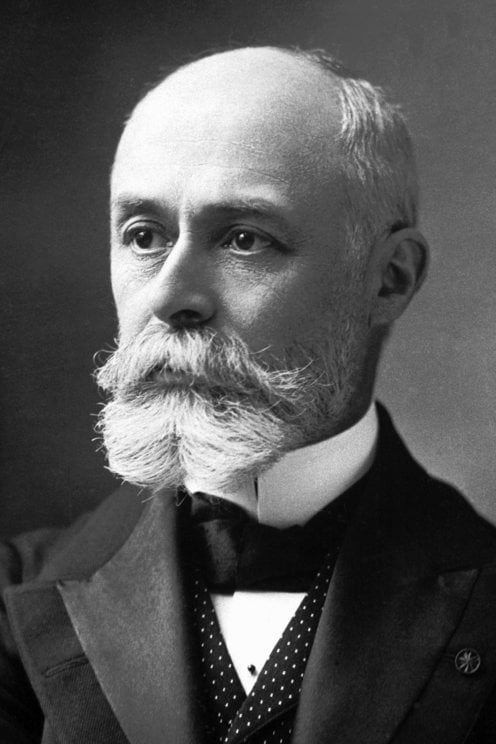



Henri Becquerel Facts Nobelprize Org




Suppose You Could Go Back In Time To Interview Henri Becquerel On The Day He Discovered Brainly Com




Discovery Of Radioactivity A Pure Accident In Hindi Youtube



Aucun commentaire:
Publier un commentaire